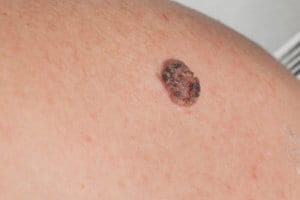
Mohs Reconstruction
A Mohs surgeon is a doctor with special training in removing skin cancer, usually a dermatologist. They are able to remove the cancer in small pieces, and then look at each small piece under the microscope to see if the sample contains cancer. Doing this helps them make sure they get all the cancer, but only take the cancer and not the normal skin around it. Mohs surgery is best for squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma.
After Mohs surgery, there is a hole in the skin where the cancer was removed. If it is small, it can often be closed by the Mohs surgeon at the same time. When the defect is large, many Mohs surgeons will ask a facial plastic surgeon to help. The facial plastic surgeon can help to close the wound in the most cosmetic way possible. They may move some of the skin and tissue around so it fills the defects, which is called a local flap. There are several different kinds of local flaps, and you may hear names like rotational flaps, transposition flaps, interpolated flap. Or it may be done by taking a small piece of skin from another area and sewing it into the defect, this is called a skin graft. At your appointment, the facial plastic surgeon will discuss with you what type of procedure will work best for you.
Wide Local Excision Skin Cancer Surgery
There are some types of skin cancer that are difficult to do with Mohs surgery, melanoma is one. In these cases it is better to have the lesion surgically removed and take a small cuff of normal tissue around it to make sure that all the cancer is removed. This type of surgery can be done by a facial plastic surgeon and can usually be done in our office. After we are sure that all the cancer is removed, we can help reconstruct the defect in a way that is similar to Mohs reconstruction.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
For some large melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas there is chance that the cancer had spread from the skin into the lymph nodes. Previously, doctors would do a big surgery that removed all the lymph nodes from the area and then checked to see if there was cancer in them. Now we have learned that the cancer usually spreads to one nearby lymph node, called the “sentinel node” first, then later spreads to other nodes. What we are able to do now is the find the first lymph node in the chain (sentinel) node and remove only that one. If there is no cancer in that node, then there is a very good chance that there is no cancer in any of the lymph nodes. The benefit of doing this is that when the sentinel node is negative, the patient can avoid a big surgery.
There are many treatments and different options that people learn when they find they have skin cancer. It can be overwhelming to process all the information. At your visit with us, we will explain the plan and we can work together to find a reconstructive solution.