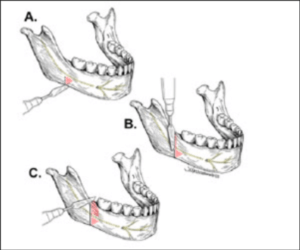
Dr. Boutros and his team have pioneered the techniques of endoscopic mandibular distraction. Unlike earlier techniques that required large incisions on our patients faces, endoscopic techniques use a minimally-invasive approach through the inside of the mouth. As a result, the patient has almost no risk of injury to their delicate facial nerve.